High-speed magnetic motor rotor assemblies utilizing power-dense permanent magnet materials represent a significant advancement in the field of electrical machinery, particularly in applications such as electric motors and generators. These assemblies are at the heart of high-efficiency and compact designs for a wide range of industries, including automotive (electric vehicles), aerospace, and industrial automation. Let’s delve into some key aspects.
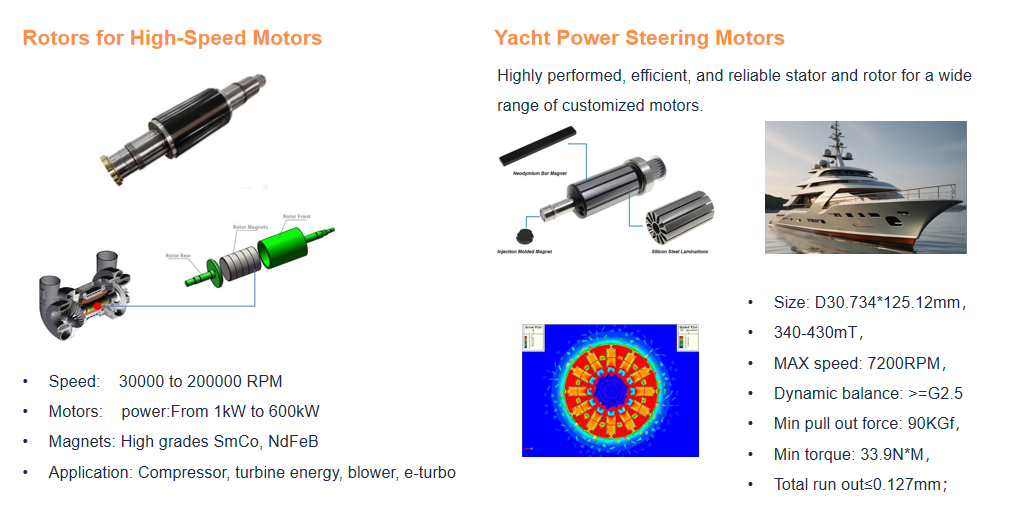
Key Components and Materials
Permanent Magnet Materials:
Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB): Offers the highest available magnetic energy density, making it ideal for compact, high-power applications.
Samarium Cobalt (SmCo): Known for its high-temperature stability and resistance to demagnetization, suitable for applications involving high operating temperatures or requiring long life under harsh conditions.
Rotor Design:
Laminated Steel Core: Reduces eddy current losses, which are significant at high speeds. The lamination of the steel core is crucial for high-efficiency rotors.
Retention Sleeves: High-speed operation subjects the rotor to significant centrifugal forces. Materials like carbon fiber or other composites are used as retention sleeves to hold the magnets in place securely.

High Efficiency: The use of high-energy-density magnets allows for smaller, more efficient motors that generate less waste heat.
Compact Size: High power density enables smaller motor sizes for a given power output, critical for applications with space constraints.
High Torque-to-Weight Ratio: Ideal for applications requiring high performance and efficiency, such as aerospace and electric vehicles.
Reduced Energy Consumption: Enhanced efficiency leads to lower energy consumption, crucial for battery-powered applications.
Durability and High-Temperature Performance: Materials like SmCo allow these rotors to operate reliably under high temperatures and harsh conditions.
Challenges and Solutions
Thermal Management: High-speed operation can generate significant heat. Advanced cooling methods, such as liquid cooling or the use of thermally conductive materials, are employed to manage this.
Centrifugal Forces: At high speeds, the centrifugal force can be substantial. Using high-strength materials for the retention system is essential to ensure the magnets remain in place.
Cost and Material Availability: High-performance magnets like NdFeB and SmCo can be expensive and subject to market availability. Ongoing research aims to find more abundant, cost-effective materials with similar magnetic properties.


Future Directions
Research continues into finding new materials and improving existing ones to enhance the performance and reduce the costs of high-speed permanent magnetic rotor assemblies. Techniques such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) are being explored for producing complex rotor geometries more efficiently. The development of these assemblies is critical for the advancement of electric motors and generators, driving forward innovations in many technology sectors.







































