What is a resolver?
Resolver is the current domestic professional name, referred to as "rotating change". Because the basic principle of its work is the Transformer, the air gap of the "transformer" on the stator changes periodically during the work process by rotating the rotor, and then forms the function of monitoring the angular displacement (speed and position) of the motor rotor, so its full name is rotating transformer, which can also be translated into Rototary Transformer. However, this name is rarely used in English, and the general English name is Resolver.
The Working Principle of Sensor Resolvers
Overview
Sensor Resolvers are a type of electromagnetic sensor used to measure the angular position of a rotating element relative to a fixed reference. They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, utilizing the interaction between a rotating primary winding (or rotor) and a stationary secondary winding (or stator) to generate an output signal proportional to the angular position.
Key Components
Rotor (Primary Winding): The rotating part of the resolver, which contains one or more coils of wire. As the rotor turns, it creates a changing magnetic field that interacts with the stator.
Stator (Secondary Winding): The stationary part of the resolver, containing one or more coils of wire arranged to intersect the magnetic field created by the rotor. The stator coils generate an output signal that varies with the angular position of the rotor.
Working Principle
Excitation: An AC excitation signal is applied to the rotor coils. This creates a rotating magnetic field within the resolver.
Electromagnetic Induction: As the rotor turns, the changing magnetic field induces an AC voltage in the stator coils. The amplitude and phase of this induced voltage depend on the angular position of the rotor relative to the stator.
Signal Processing: The output signal from the stator coils is typically a sinusoidal wave with an amplitude and phase that vary with the rotor's angular position. This signal is then processed by a resolver-to-digital converter (RDC) or similar device to determine the exact angular position of the rotor.
Absolute Positioning: Sensor Resolvers provide absolute position information, meaning they can determine the angular position of the rotor without the need for a reference point or home position.
Advantages
High Accuracy: Sensor Resolvers offer high accuracy and precision in measuring angular position.
Ruggedness: They are designed to withstand harsh environments and can operate reliably in high temperatures, vibrations, and shocks.
Electromagnetic Immunity: Unlike some other sensors, Sensor Resolvers are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Longevity: Their contactless design eliminates wear and tear, resulting in long service life and low maintenance requirements.
Applications
Sensor Resolvers are widely used in various industrial and automotive applications, including:
Electric motor control
Servo systems
Robotics
Aerospace and defense
Heavy machinery
Process control systems
In summary, Sensor Resolvers work by utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction to measure the angular position of a rotating element. Their high accuracy, ruggedness, and immunity to EMI make them an ideal choice for a wide range of industrial and automotive applications.
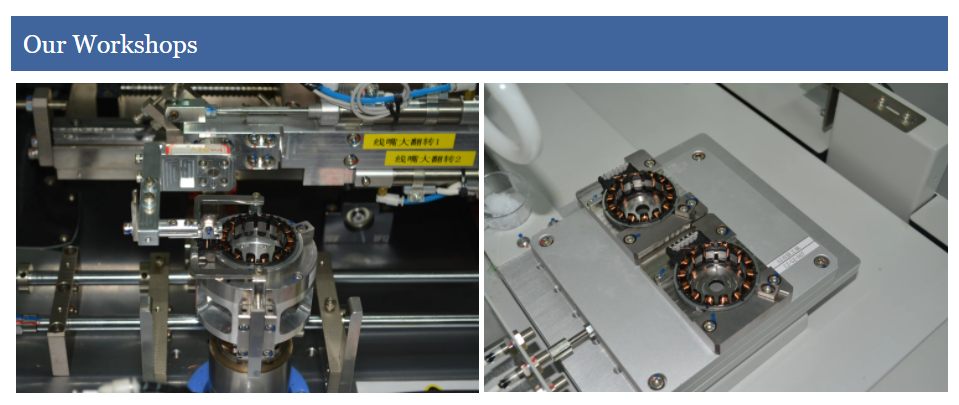
100% full inspection of production line
MES system each product of all raw materials + each process + factory 100% full inspection traceability.Providing high quality products through new technologies. We know that the trust of our customers is the cornerstone of our long-term cooperation.

Strong custom development ability
Support customized according to motor design, control and other special needs. Assist the client in the overall design, analysis and optimization of the drive unit and rotation cooperation, and analysis and solution of bench test problems; Rich experience in automotive project development, manufacturing and quality management.



















