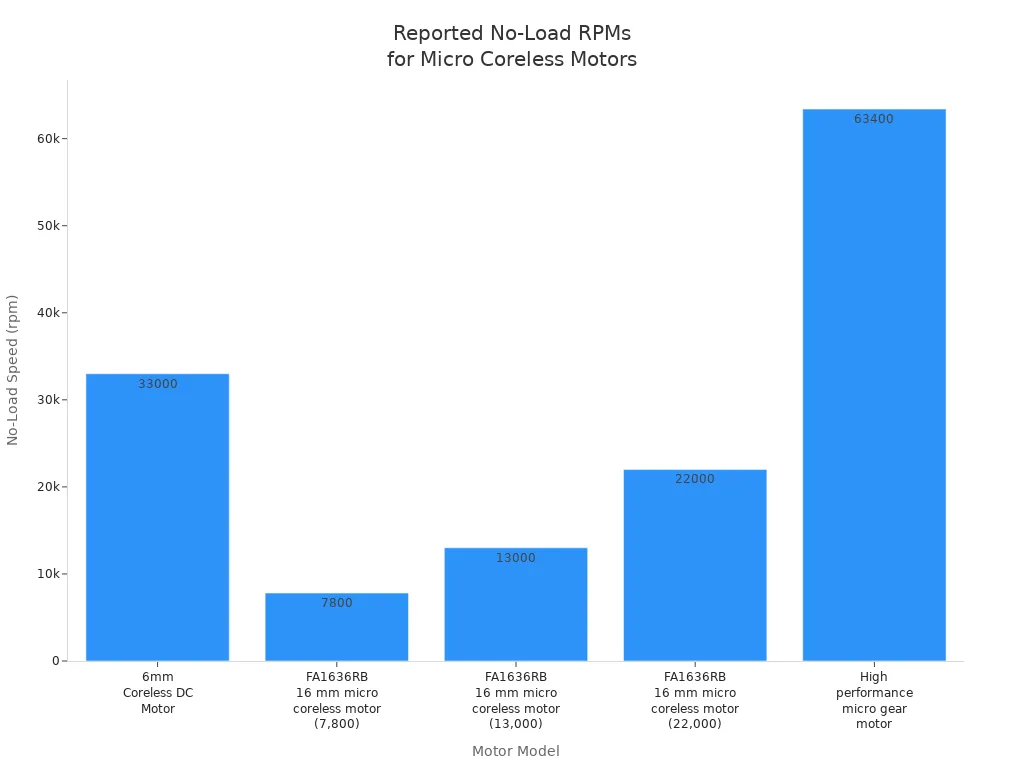
You often find that a micro coreless motor spins at speeds from about 20,000 to 66,000 rpm when powered by 3 to 4 volts. Rpm stands for revolutions per minute, which tells you how fast the motor’s shaft turns. This speed matters because it affects how much power your device can deliver. For example, the table below shows real-world rpm numbers for different models.
Model |
No-Load Speed (rpm) |
6mm Coreless DC Motor |
33,000 ± 10% |
FA1636RB 16 mm micro coreless motor |
7,800, 13,000, 22,000, 22,000 |
High performance micro gear motor |
63,400 |
Key Takeaways
Micro coreless motors usually spin from 20,000 to 66,000 rpm. They need 3 to 4 volts to work. Look at the specifications to know your motor’s exact speed.
No-load rpm is higher than loaded rpm. If you add weight or resistance, the motor slows down. Always think about the load when picking a motor for your project.
Giving the motor more voltage makes it spin faster. Use the right voltage so you do not break the motor. This helps you get the speed you want.
Use a tachometer to check the motor’s rpm exactly. You can also use DIY ways like optical sensors or apps to check the speed.
Picking the right rpm is very important for your device. Different things, like drones or medical devices, need certain speeds to work best.
Micro Coreless Motor RPM Range
Typical RPM Values
You can find a wide range of rpm values when you look at micro coreless motors. Most models run between 20,000 and 66,000 rpm when powered by 3 to 4 volts. Some motors designed for RC drones or high-speed applications reach even higher speeds. Here are some examples:
A micro coreless motor used in RC drones can reach up to 10,230 rpm at 24 volts with a continuous current of 566mA.
Many standard micro coreless motors spin at 33,000 rpm or more under no-load conditions.
High-performance models may achieve speeds above 50,000 rpm.
You should always check the specifications for your motor. Manufacturers list the no-load speed, which shows how fast the motor spins without any resistance.
No-Load vs. Loaded RPM
When you use a micro coreless motor, you will notice a difference between no-load rpm and loaded rpm. No-load rpm means the motor spins freely, with nothing slowing it down. Loaded rpm happens when you attach a propeller, gear, or other device that creates resistance.
The rpm drops when you add a load because the motor works harder to overcome resistance. The back EMF (electromotive force) decreases, which lowers the speed. The motor slows down until the current and torque balance with the load.
Here is what you can expect:
No-load rpm is always higher than loaded rpm.
The speed drops as you increase the load.
The exact decrease depends on the size of the load and the motor’s design.
If you want your device to run at a certain speed, you need to consider both the no-load and loaded rpm. This helps you choose the right micro coreless motor for your project.
Factors Affecting RPM
Voltage Impact
The voltage you supply to a micro coreless motor has a big effect on its speed. When you increase the voltage, the rpm goes up. If you lower the voltage, the motor spins slower. Most mini DC motors work best between 1.5 and 100 volts. Common choices are 3V, 6V, or 12V. For example, if you use a 3V battery, the motor will spin at a certain speed. If you switch to a 6V battery, the rpm will rise. This happens because more voltage pushes more current through the motor, making it turn faster.
Tip: Always check the recommended voltage for your motor. Too much voltage can damage it, while too little may not give enough speed.
Load Effects
The load is anything the motor has to move, like a propeller or a gear. When you add a load, the rpm drops. The motor works harder to turn the extra weight. If you add a heavy load, the speed drops even more. For example, a micro coreless motor spinning freely might reach 33,000 rpm. If you attach a small fan, the speed could drop to 28,000 rpm. A bigger fan would slow it down even further.
More load = lower rpm
Less load = higher rpm
You should always think about the load when you pick a motor for your project.
Motor Design
The design of the motor also affects its rpm. A micro coreless motor uses a lightweight, coreless coil. This design gives it some special features:
Quick acceleration and high efficiency because of the lightweight build
Low inertia, which means the motor responds fast to changes in speed
Smooth and steady operation, thanks to reduced cogging torque
High power output in a small size, which helps in tight spaces
Motors with strong magnets, special winding types, and small rotors can spin faster. The coreless design also means less noise and a smoother speed curve. You will see these benefits in devices like drones, medical tools, and robotics, where speed and control matter most.
Measuring RPM
Tachometer Use
A tachometer helps you find out how fast a motor spins. This tool shows the speed right away and is very accurate. Some digital tachometers use a laser to check movement. You point the laser at a shiny spot on the motor. The screen then shows the rpm number. These tachometers can measure speeds from 10 to 99,999 rpm. They work from about 50mm to 200mm away. You do not have to touch the motor, so there is no extra drag.
Feature |
Description |
Type |
Non-contact digital tachometer |
RPM Measurement Range |
10.0 to 99,999 RPM |
Measurement Method |
Non-intrusive, using laser |
Display |
LCD Backlight, shows RPM and revolution count |
Target Distance |
50mm to 200mm |
Battery Life |
Continuous operation for 12 hours |
If you need more exact results, you can use a DC tachometer generator. This tool changes the spinning speed into a voltage signal. It is good for labs and servo systems.
DIY Methods
You can check rpm at home or in class in many ways. You might use an optical sensor to spot marks on the spinning shaft. You could build an RPM counter with counters and LED numbers. Some phone apps use your camera to figure out rpm.
Tip: Optical sensors and phone apps are fast and easy to use. You do not need special tools, and setup is simple.
You can also use a proximity sensor or check the back EMF for a cheap way to measure speed. Counting with a fast clock helps you get good results, even at slow speeds.
Calculating from Specs
You can guess rpm using the Kv rating and the voltage you use. The Kv rating tells you how many times the motor spins for each volt. Here is a simple formula:
RPM = Kv × Voltage
For example, if your motor has a Kv of 1000 and you use 10 volts, the rpm is 10,000. If you have a 2300Kv motor and a 14.8V battery, the rpm is about 34,040. Always look at the maker’s data for the best answer. This way, you can know the speed before you turn on your micro coreless motor.
Why RPM Matters
Performance
RPM is important for how well your motor works. If you use a micro coreless motor, you want it to move fast and smooth. A higher rpm lets the motor react quickly. This is good for things that need speed and accuracy, like robots or small gadgets. The table below shows how rpm changes performance:
Specification |
Value |
Rated Voltage |
3.0V |
Rated Speed |
14,000 ± 2,500 rpm |
Dimensions |
11.9mm x 4.6mm x 4.9mm |
Application Suitability |
Robotics and miniaturized electronic devices |
Impact on Performance |
Higher RPM leads to quicker actuation and responsiveness, crucial for precision and rapid movement. |
You get more than just speed with these motors. Micro coreless motors start and stop quickly. They give strong power in a small size. They run smoothly, so you can control them easily. These motors also handle heat well, which helps them last longer.
Feature |
Explanation |
Rotation Speed |
Goes up with more input pulses; slow speeds can cause problems. |
Load Torque Impact |
Heavy loads make the motor spin slower. |
Voltage Application |
More voltage makes the motor spin faster. |
Note: High rpm can mean less torque and more power use. You need to balance speed with strength and efficiency.
Performance Factor |
Description |
High RPM |
Coreless motors can go very fast but need careful use to avoid damage. |
Torque |
If rpm goes up, torque can go down. |
Power Consumption |
Faster speeds use more power, which can lower efficiency. |
Application Fit
You need to pick the right rpm for your project. Different devices need different speeds. Drones need high rpm to spin fast and lift off. Medical devices need motors that are quiet and steady. Toys need motors that are safe and not too fast. The table below shows how rpm fits each use:
Application |
RPM Range |
Key Features |
Drones |
Up to 30,000 |
High power-to-weight ratio, lightweight, high efficiency for extended flight. |
Medical Devices |
Varies |
Low noise, precise control, reliability for critical tasks. |
Toys |
Up to 33,000 |
Compact size, efficient operation for remote control and models. |
Drones: High rpm helps them lift and move fast.
Medical devices: Lower rpm keeps them quiet and steady.
Toys: Medium rpm makes them fun and safe.
Always check what rpm your project needs. Picking the right speed helps your device work well and last longer.
You have learned that micro coreless motors spin from 20,000 to 66,000 rpm. The speed depends on voltage, load, and how the motor is built. Always look at the datasheet to find the rated rpm. You should also measure the speed for your project. The table below shows the main points:
Key Aspect |
Details |
RPM Range |
20,000–66,000 rpm typical |
Influencing Factors |
Voltage, load, motor design |
Measurement |
Tachometer, DIY, or calculation |
Application Fit |
Drones, medical, robotics, toys |
Make sure the rpm matches what your project needs. Picking the right kv and checking the specs can stop motor problems.
FAQ
What does "coreless" mean in a micro motor?
A coreless motor uses a coil without an iron core. You get faster response and less weight. This design helps the motor spin quickly and smoothly.
Can you control the rpm of a micro coreless motor?
Yes, you can control rpm by changing the voltage or using a motor controller. Lower voltage slows the motor. Higher voltage makes it spin faster.
Why does the rpm drop when you add a load?
When you add a load, the motor works harder. The speed drops because the motor needs more power to turn the extra weight. You see lower rpm with heavier loads.
How do you know if your motor is spinning too fast?
You may notice extra heat, noise, or vibration. The motor might not last as long. Always check the manufacturer's rpm limit to keep your motor safe.
What happens if you use too much voltage?
Too much voltage can overheat the motor. You might damage the windings or shorten the motor’s life. Always use the recommended voltage for safe operation.