Reluctance resolvers, as high-precision angle sensors, play an indispensable role in fields such as industrial automation, new energy vehicles, and humanoid robots. Faced with a dazzling array of product models on the market, selecting the right reluctance resolver has become a necessary skill for engineers. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the key selection points for reluctance resolvers, focusing on the two critical parameters of size and pole pair count, helping you understand their impact on performance and how to make the best choice based on the application scenario. From ultra-thin designs to high pole pair configurations, from temperature adaptability to shock resistance, we will systematically introduce various factors to consider during the selection process and provide typical application cases to help you find the most suitable solution among the complex array of product models.
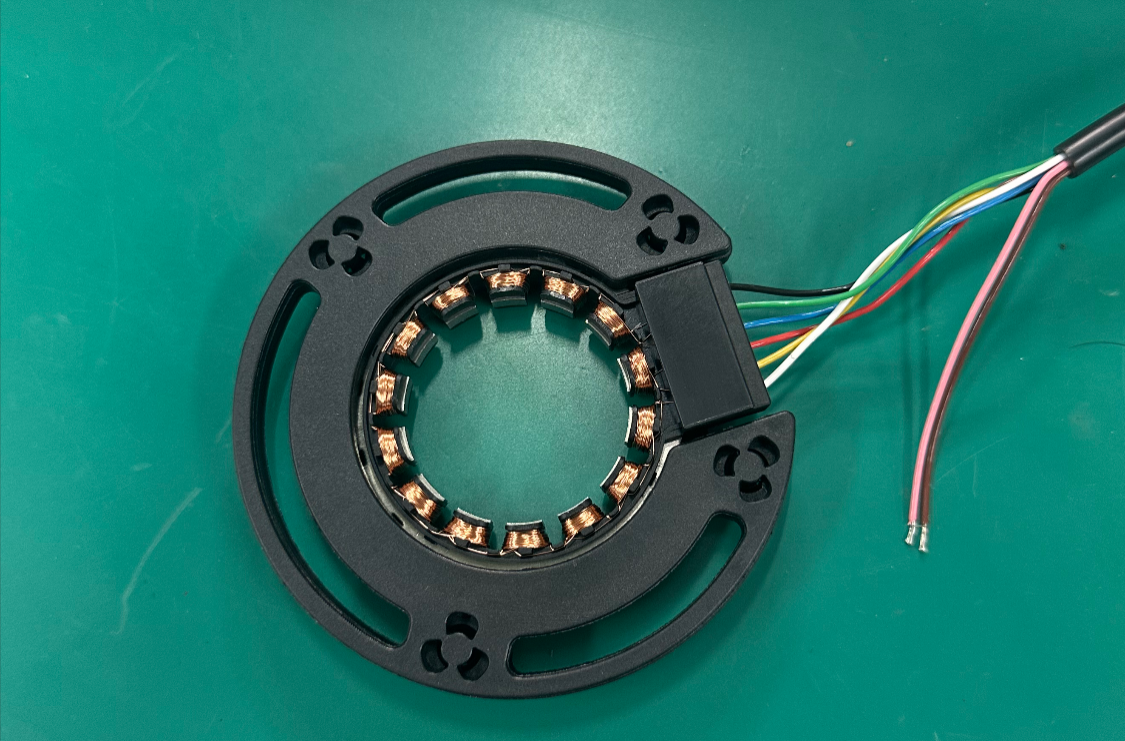
Overview and Working Principle of Reluctance Resolvers
A reluctance resolver is a non-contact angle sensor based on the magneto-resistive effect. It converts mechanical rotation angles into electrical signal outputs through the principle of electromagnetic coupling. Compared to traditional wound resolvers, reluctance resolvers are increasingly favored in modern industrial applications due to their simple structure, high reliability, and cost advantages. These sensors can operate stably within a wide temperature range of -55°C to +155°C, feature high protection ratings, resist vibration and shock, achieve maximum speeds of up to 60,000 RPM, and offer extremely high reliability due to their rotor's lack of windings.
The basic working principle of a reluctance resolver involves using the relative rotation between the rotor and stator to change the magnetic reluctance of the magnetic circuit, thereby inducing voltage signals related to the rotation angle in the secondary windings. When an AC excitation current (typically 7V, 10kHz) is applied to the primary winding, an alternating magnetic field is established in the air gap. The rotor's salient pole structure rotates with the shaft, causing periodic changes in magnetic reluctance, which in turn generates two sinusoidal and cosine signals with a 90° phase difference in the secondary windings. By decoding the amplitude ratio or phase relationship of these two signals, the absolute angular position of the rotor can be precisely determined.
The core advantages of reluctance resolvers lie in their non-contact sensing characteristic, which eliminates brush wear issues and significantly extends service life; simultaneously, they provide absolute position detection, eliminating the need for re-homing after power loss; furthermore, their high dynamic response capability (up to 10kHz or more) makes them非常适合 (very suitable - ideal) for high-speed motion control scenarios. These characteristics make reluctance resolvers an ideal choice for applications such as servo systems, robot joints, and electric vehicle traction motors.
Key Factors in Size Selection
Size selection for reluctance resolvers is the primary consideration in the selection process, directly affecting the equipment's spatial layout and mechanical compatibility. The demand for sensor miniaturization in modern industrial applications is growing, especially in space-constrained scenarios like robot joints and electric vehicle motors, where ultra-thin, compact designs often become a necessity.
Dimensions and Mounting Methods
The size parameters of reluctance resolvers mainly include outer diameter, inner bore diameter, and axial length. Common series on the market, such as the 52 series, 132 series, and 215 series, represent different size specifications. The following factors need comprehensive consideration during selection:
· Mounting Space:
Measure the three-dimensional dimensions of the available space to ensure the resolver can be installed smoothly without interfering with other components. Applications like robot joints often require ultra-small resolvers with diameters less than 60mm.
· Shaft Diameter Matching:
The resolver's inner bore diameter must precisely match the motor or equipment shaft. Too large a bore causes unstable mounting, while too small prevents assembly. Standard products usually offer multiple bore options and can also support customization.
· Axial Length:
In applications with height restrictions (e.g., flat motors), models with short axial lengths must be chosen. Some ultra-thin designed resolvers can have an axial height controlled within 15mm.
· Mounting Interface:
Confirm whether the resolver's mounting flange type (e.g., pilot locating, threaded hole fixing) is compatible with the host machine. Incompatible interfaces lead to the need for additional adapters, increasing system complexity and cost.
Considerations for Environmental Adaptability
Size selection must also be comprehensively evaluated in conjunction with the special requirements of the working environment. Different application scenarios have different standards for the resolver's environmental adaptability:
· Temperature Range:
Standard reluctance resolvers typically support an operating temperature range of -55°C to +155°C, sufficient for the vast majority of industrial applications. However, in extreme environments (e.g., aerospace or deep-well equipment), special materials or designs may be required.
· Protection Rating (IP):
Choose an appropriate IP rating based on the levels of dust and humidity in the application environment. Dusty environments like textile machinery often require IP54 or higher, while automotive applications may require IP67.
· Vibration Resistance:
For occasions with strong vibrations, such as construction machinery or aerospace, models with reinforced structures must be selected.
· Speed Capability:
The typical maximum speed for reluctance resolvers is 60,000 RPM, but the impact of centrifugal force on the structure must be considered in practical applications. Models that have undergone dynamic balancing should be selected for high-speed scenarios.
Size Considerations for Special Application Scenarios
Certain special applications have unique requirements for resolver size, requiring particular attention:
· Internal Mounting Applications:
When the resolver needs to be built inside the motor, the available space must be measured precisely, and the impact of heat dissipation considered. Internal structures often use
frameless designs to minimize axial size.
· Humanoid Robot Joints:
Humanoid robot joints have extremely limited space and require high-precision control. Suppliers like Huaxuan Sensing have specifically developed small-size resolvers adapted for robot joints, significantly reducing volume while maintaining performance.
· Automotive E-Drive Systems:
Traction motor resolvers for new energy vehicles need to withstand high temperatures and high vibration environments while meeting automotive-grade reliability standards. Such applications often require customized compact designs.
Selection of Pole Pairs and Performance Impact
Pole pair count is one of the core parameters of a reluctance resolver, directly affecting the sensor's angular resolution, accuracy, and electrical characteristics. The pole pair count refers to the number of magnetic pole pairs on the resolver's rotor, determining the number of electrical cycles output per revolution. Common pole pair configurations for reluctance resolvers on the market include 2-pole pair, 3-pole pair, 4-pole pair, and 12-pole pair, etc., with different pole pairs适应 (suitable for - suiting) different application needs.
Relationship Between Pole Pairs and Angular Resolution
There is a direct correlation between the pole pair count and the resolver's angular resolution. Theoretically, an n-pole pair resolver can magnify the mechanical angle by a factor of n for measurement, thereby improving the electrical angular resolution. The specific relationship is:
· Electrical Angle = Mechanical Angle × Pole Pair Count
· Angular Resolution Improvement Factor = Pole Pair Count
For example, a 4-pole pair resolver magnifies the mechanical angle by 4 times, meaning the same electrical measurement system can achieve higher effective resolution. For applications requiring high-precision position detection, such as CNC machine tools or precision robot joints, choosing a resolver with a higher pole pair count can significantly enhance system control accuracy.
However, increasing the pole pair count also brings some technical challenges:
· Increased signal processing complexity, requiring higher-performance decoding circuits.
· Higher frequency signals are more susceptible to noise interference.
· Higher mechanical machining precision requirements, increasing manufacturing costs.
· Maximum speed may be limited (due to increased iron losses).
Typical Application Scenarios for Different Pole Pairs
The choice of pole pair count varies significantly based on the application's different needs for accuracy and speed:
· 2-Pole Pair Resolvers:
Suitable for applications that do not require high resolution but need
high speed, such as some industrial pumps or fans. These resolvers have a simple structure, lower cost, and can reach maximum speeds of 60,000 RPM.
· 4-Pole Pair Resolvers:
A general-purpose choice, balancing accuracy and speed requirements, widely used in textile machinery, electronic cams, injection molding machines, and CNC machine tools.
· 12-Pole Pair Resolvers:
Provide higher
angular resolution, suitable for precision servo systems, military equipment, and high-end industrial automation equipment. The electrical signal change per mechanical angle is more significant for these resolvers, which helps improve control accuracy.
· Ultra-High Pole Pair Resolvers:
Certain special applications (e.g., astronomical instruments, precision measuring equipment) may require configurations of 16 pole pairs or even higher, usually needing customized design to balance resolution and signal integrity.
Collaborative Consideration of Pole Pairs with Other Parameters
The selection of pole pair count cannot be done in isolation; it must be evaluated collaboratively with other resolver parameters:
· Excitation Frequency:
The nominal excitation frequency for most reluctance resolvers is 10kHz. When the pole pair count increases, the output signal frequency increases proportionally (Output Frequency = Pole Pairs × RPM). It must be ensured that this does not exceed the resolver-to-digital converter's (RDC's) processing capability.
· Accuracy Indicators:
Resolvers with higher pole counts often have higher nominal accuracy (e.g., ±30 arc-minutes vs. ±60 arc-minutes).
· Phase Shift:
The phase shift characteristics differ for resolvers with different pole pairs, which can affect the control system's compensation strategy.
· Input Impedance:
Changing the pole pair count affects the electrical parameters of the windings.
Industrial Automation Field
In industrial automation equipment, reluctance resolvers primarily undertake position feedback and speed detection functions, serving as core components of servo systems:
· CNC Machine Tools:
High-precision machining requires resolvers with high angular resolution and repeatable positioning accuracy. Models with 4 pole pairs or higher are typically chosen. Size considerations involve integration with the servo motor, where ultra-thin designs are often preferred.
· Injection Molding Machines:
These applications involve high ambient temperatures and vibrations, requiring resolvers with good
temperature resistance and
vibration resistance. Models with medium pole pairs (2-4) strike a balance between accuracy and cost, and a protection rating of IP54 or above is usually required.
· Electronic Cams:
Electronic cam systems, which replace mechanical cams, rely on high dynamic response position detection. The delay-free characteristic of reluctance resolvers makes them an ideal choice, typically using a 4-pole pair configuration for good motion curve control capability. Size needs to be customized based on the spatial constraints of the cam mechanism.
New Energy Vehicle Field
The electric drive systems of electric and hybrid vehicles place stringent demands on resolvers, driving the rapid development of reluctance resolver technology:
· Traction Motors:
As core sensors in electric vehicles, traction motor resolvers need to withstand high temperatures and high vibration environments while meeting automotive-grade reliability standards. The 132 series (4-pole pair) and 52 series are widely used by domestic new energy vehicle manufacturers. Their operating temperature range of -55°C to +155°C and speed capability of 60,000 RPM fully meet automotive drive requirements.
· Power Steering Motors (EPS):
Steering systems have extremely high safety requirements.
Dual redundancy design provides an ideal solution for such applications. This design allows automatic switching to a backup winding if the primary winding fails, ensuring continuous system operation. Compact designs are typically used size-wise to adapt to limited installation space.
· Battery Cooling Pumps:
These auxiliary systems are cost-sensitive but have relatively low accuracy requirements. 2-pole pair reluctance resolvers are a common choice due to their high cost-effectiveness, and their simple structure also enhances reliability in fluid environments.
Humanoid Robots and Special Applications
In recent years, with breakthroughs in bionic robot technology, reluctance resolvers have found important application scenarios in this emerging field:
· Joint Position Detection:
Humanoid robot joints require extremely high position accuracy and dynamic response. Suppliers are migrating automotive resolver technology to the robotics field, developing specialized small-size, high pole pair models. These resolvers can provide real-time, accurate angle feedback when robots perform challenging movements like jumping or rolling.
· Force Control and Safety Monitoring:
In collaborative robots (cobots), resolvers not only provide position information but also work with force sensors to achieve
safety control. By monitoring joint position changes in real-time, the system can quickly identify abnormal loads or collisions and trigger a safety shutdown mechanism. Such applications typically require configurations above 4 pole pairs for sufficient sensitivity.
· Space and Special Robots:
Robots in extreme environments, such as spacecraft manipulators or deep-sea exploration equipment, require specially designed resolvers. Beyond常规 (conventional - standard) size and pole pair considerations, attention must be paid to material properties like radiation resistance and pressure resistance. These applications often require fully customized solutions.
Selection Process and Common Misconceptions
Selecting a reluctance resolver is a technical task requiring systematic thinking and comprehensive evaluation. A reasonable selection process can avoid many problems in subsequent applications. Simultaneously, understanding common misconceptions helps engineers avoid pitfalls and make more scientific choices. From defining requirements to verification testing, each step needs rigorous attention to ensure the selected resolver achieves the optimal balance between performance, reliability, and cost.
Systematic Selection Process
A complete reluctance resolver selection process typically includes the following key steps:
1. Application Requirement Analysis
Define mechanical mounting conditions (space, shaft diameter, interface)
Determine motion parameters (speed range, acceleration)
Evaluate environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, vibration, EMI)
Define accuracy requirements (resolution, linearity, repeatability)
Consider safety and redundancy needs (e.g., for automotive, aerospace applications)
2. Preliminary Parameter Screening
Determine size range based on space constraints (outer diameter, length)
Select pole pair count based on speed and accuracy requirements
Consider electrical interface compatibility (excitation voltage, signal type)
Evaluate protection rating and material requirements
3. Supplier and Technical Solution Evaluation
Compare standard product parameters and customization capabilities of different manufacturers
Examine the completeness of technical documentation (drawings, specifications, certifications)
Verify supply chain stability and delivery lead times
Evaluate cost and cost-effectiveness
4. Sample Testing and Verification
Mechanical compatibility check (dimensions, mounting)
Electrical performance testing (signal quality, accuracy)
Environmental adaptability verification (temperature, humidity, vibration)
Life and reliability assessment
5. Final Decision and Volume Procurement
Determine the final model based on comprehensive test results
Confirm measures for batch supply quality consistency
Establish long-term technical support channels
Common Misconceptions in Size Selection
During the size selection process for reluctance resolvers, engineers can easily fall into the following misconceptions:
· Ignoring Mounting Tolerances:
Considering only theoretical size matching while ignoring actual machining tolerances, leading to installation difficulties. It is recommended to reserve appropriate assembly clearance and consider the effects of thermal expansion.
· Over-Pursuit of Miniaturization:
While ultra-thin designs save space, they may sacrifice
structural strength and
heat dissipation performance. The cost of size reduction must be carefully evaluated in high-speed or high-temperature applications.
· Neglecting Future Maintenance:
Choosing overly compact mounting methods may increase difficulty in later maintenance. The convenience of initial installation should be weighed against the total lifecycle maintenance cost.
· Insufficient Interface Standardization:
Using non-standard interfaces increases system complexity and spare parts management difficulty. Try to choose industry-standard interfaces or at least standardize within the enterprise.
Common Misconceptions in Pole Pair Selection
Typical misconceptions also exist in the selection of pole pairs, requiring special attention:
· Blind Pursuit of High Pole Pairs:
Believing that higher pole pairs are always better. In reality, high pole pairs increase signal processing difficulty and cost, resulting in waste in applications that do not require extremely high precision.
· Ignoring Speed Limitations:
Increasing pole pairs raises the output signal frequency, which may exceed the resolver-to-digital converter's processing capability. Ensure the system's electronics can support the signal frequency at the maximum speed for the selected pole pair count.
· Overlooking Temperature Effects:
The temperature characteristics of resolvers with different pole pairs may differ; signal attenuation in high pole pair models might be more pronounced in high-temperature environments. Performance consistency across the full temperature range needs verification.
· Disregarding System Compatibility:
Changing the pole pair count may require adjustments to control system parameters (e.g., filter settings, compensation algorithms); otherwise, it could lead to performance degradation or even instability.
Other Comprehensive Considerations
Beyond the two core parameters of size and pole pair count, reluctance resolver selection must also comprehensively consider the following factors:
· Electrical Parameter Matching:
Excitation voltage (typically 7V AC), frequency (commonly 10kHz), input impedance, etc., need to be compatible with the existing system. Mismatches can lead to degraded signal quality or the need for additional interface circuits.
· Environmental Adaptability:
Choose appropriate temperature grades (Industrial -20~85°C, Automotive -40~125°C, Military -55~155°C), protection ratings (IP54, IP67, etc.), and materials (e.g., corrosion-resistant coating) based on the application environment.
· Standards and Certifications:
Different industries have specific certification requirements (e.g., AEC-Q200 for automotive, CE marking for industrial equipment). Lack of necessary certifications may prevent the product from entering the target market.
· Supplier Technical Support:
A good supplier can not only provide products but also value-added services such as
selection support,
customization services, and
failure analysis.
Selection Decision Support Tools
To aid selection decisions, engineers can utilize the following tools and methods:
· Parameter Comparison Table:
List and compare key parameters (size, pole pairs, accuracy, temperature range, etc.) of candidate models, using weighted scoring.
· Simulation Verification:
Use tools like MATLAB/Simulink to simulate the resolver's performance in the target system and predict potential issues.
· Cost Analysis Model:
Consider not only procurement cost but also total lifecycle costs including installation, maintenance, spare parts, and potential downtime losses.
· Prototype Test Platform:
Set up a representative test environment to validate candidate models under actual operating conditions, collecting performance data to support the final decision.
With technological advancements, the design and manufacturing processes of reluctance resolvers continue to innovate. There is no "one-size-fits-all" best choice, only the solution most suitable for the specific application. By following a systematic selection process, avoiding common misconceptions, and comprehensively considering. technical, cost, and supply chain factors, you can select the most appropriate reluctance resolver for your project.





















